How Do Crypto Exchanges Generate Revenue Even In A Turbulent Market?

Cryptocurrency exchanges have demonstrated remarkable resilience during market downturns, unlike institutional investors and individual traders. This is attributed to their role as market makers, fostering trader and institutional activity, and charging fees for their services. This article will outline the financial performance of crypto exchanges, exploring their primary revenue streams and the intricacies involved in generating profits through these means.
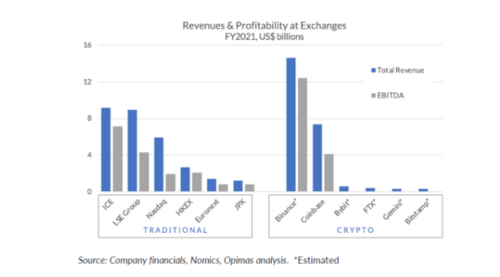
According to a financial services consultancy Opimas report, cryptocurrency exchanges made $24.3 billion in global trading revenue in 2021. This is the first time that the revenue generated by cryptocurrency exchanges has exceeded that of traditional stock exchanges such as the New York Stock Exchange and the Nasdaq.
The revenue generated by cryptocurrency exchanges was estimated to have increased by 7X compared to the $3.4 billion in sales reported in 2020. Moreover, it was found that the revenue from these exchanges surpassed that of traditional securities exchanges by approximately 60%, which totaled around $15.2 billion.
In just one year, there has been a significant change in the revenue dynamics between traditional exchanges and cryptocurrency exchanges. Previously, well-established and respected entities such as the New York Stock Exchange, Nasdaq, Deutsche Borse, and CME were generating 4X more revenue compared to their crypto counterparts. However, the tables have turned, as Binance has left these traditional exchanges far behind in performance and growth.
Source: Marketwatch
What Is A Crypto Exchange?
A cryptocurrency exchange is an online platform where individuals can trade different digital currencies, either for other cryptos or traditional fiat currencies. These exchanges provide an alternative method for obtaining cryptocurrencies, aside from methods such as mining or receiving them through airdrops. Some well-known examples of cryptocurrency exchanges include Binance, Kraken, Coinbase, HTX (formerly Huobi Global), and OKX (formerly OKEx).
Cryptocurrency exchanges have become lucrative businesses, with some valued in the billions of dollars. The surge in interest in digital currencies has resulted in a significant increase in their valuations and revenues. Coinbase and Binance are two examples of crypto exchanges that have benefited from this trend. But have you ever wondered how these exchanges generate their substantial income? Below are some overt ways in which a crypto exchange creates revenue.
Trading Commission and Withdrawal Fees
Crypto exchanges generate profits by calculating the difference between their income and operating expenses, such as maintenance, promotion, support for liquidity levels, and taxes. The primary source of income for these exchanges comes from trading commissions charged to users (traders) for every transaction. When a trade occurs, which involves closing two opposing orders (one selling, the other buying), the exchange collects a commission from both the seller's and the buyer's orders.
For example, the exchange takes a commission from both sides with a trading commission rate of 0.1% of the order value. However, if an order is executed externally, the exchange only charges a commission from one side of the transaction.
An Active User Base is Crucial
It’s important to note for an exchange to generate revenue through trading commissions and profits, it must cultivate a thriving trading environment, which hinges on having a substantial number of active users. While tools like market makers and trading bots can help stimulate activity, they cannot replace the value of genuine traders who facilitate the exchange of assets and generate commissions.
The number of active users (AU) is a vital metric in assessing a cryptocurrency exchange's revenue-generating capabilities. Although financial information in the cryptocurrency exchange domain is limited, examining available data points, such as the number of active users, can provide valuable insights.
Over recent years, cryptocurrency exchanges have been raking in substantial profits, with Binance being a prime example. According to publicly available data, Binance has generated over $1.8 billion in trading revenue since the beginning of 2021, thanks to its 28.6 million active users. The exchange's peak trading volume for the year reached an impressive $76 billion, with commissions ranging from 0% to 0.50% depending on the volume of transactions.
It’s worth noting the figures and the time when the cryptocurrency market reached its lowest point in 2018. During that period, only 313,000 users were engaging in trading on Binance. Despite being deemed relatively low activity, the popular exchanges still managed to generate substantial profits, with Binance making $446 million. While this number may not be as impressive as the most recent data, it effectively illustrates the ability of exchanges to survive even during challenging periods.
Additionally, a crucial factor to consider is the typical trading volume of a single active user. It's reasonable to assume that the higher this amount, the greater the commission the exchange earns. However, what truly matters is the volume of trades conducted by genuine active users rather than the total trading volume, which automated trading bots can inflate to the tune of 70% or more.
Withdrawal fees are also a source of revenue for crypto exchanges. The withdrawal fee amount is influenced by several factors, such as the type of asset being withdrawn, the amount of funds being transferred, and the transfer method. Some trading platforms charge a fixed withdrawal fee, while others, usually lesser-known and newer crypto exchanges, do not charge this fee to attract new users. However, it's worth noting that charging a deposit fee is not recommended, even for well-established platforms, as it can discourage users from using the platform.
Listing Fees for New Cryptos
Fees for listing a new cryptocurrency on major exchanges range from $2 million to $5 million, with some exchanges charging as high as $10 million to 15 million. The listing price varies depending on the specific project, considering factors such as the desired service package, which could include marketing support or technical assistance. There is no standard fee for listing as it is determined on a case-by-case basis.
For cryptocurrency projects looking to expand their reach, being listed on a well-established platform can increase visibility and access to a broader pool of investors. This often leads to accelerated growth for these coins. Interestingly, some prominent cryptocurrency exchanges choose to either hide or openly express their hesitation to list lower-quality coins, often referred to as "shitcoins," on their platform.

Market Making
The Market Making (MM) function ensures that traders can execute their orders seamlessly and at competitive prices, even when there may be a lack of liquidity. This is achieved by providing additional liquidity and maintaining a stable price range, thereby preventing price gaps and ensuring that buy and sell orders can be matched without delay. For instance, if a trader wants to sell an altcoin on an exchange with low trading volume, the MM function will instantly purchase the asset, executing the sale without any issues.
Customers may have the misconception that regular traders swiftly complete transactions. However, the reality is that market makers are the ones who acquire orders for subsequent resale. These market makers are accessible on every platform and provide assurance of liquidity. Conversely, if traders were to find themselves in the opposite situation, they would have to wait weeks before encountering a buyer.
Margin Trading
Trading on margin, also known as leverage, allows traders to borrow funds from the exchange in order to amplify their buying ability. This strategy offers the potential for greater profits, but it also comes with increased risks. However, it is important to note that if a trader's prediction fails, they are not necessarily left in debt.
The leverage provided by the exchange allows traders to increase their order size. Traders are protected from losing more than they have, and the exchange is not at risk of failure. For instance, if a trader has $10,000 in their account and decides to purchase bitcoin with 5X leverage, they can buy bitcoin worth $50,000. Suppose the Bitcoin price drops and becomes more affordable. In that case, the exchange typically stops at the trader's initial $10,000 investment and alerts them with a margin call, or the opposite can also happen.
Earning Services
Cryptocurrency exchanges can profit by offering services that enable users to earn money. These services include staking, lending, and a crypto marketplace. Staking involves users locking their cryptocurrencies in a wallet to help sustain the operations of a blockchain network. Through this process, they become part of the network's consensus mechanism and receive rewards in exchange. The exchange generates income by charging a fee or taking rewards earned from staking the delegated coins.
Cryptocurrency lending allows users to loan their digital assets to other individuals or organizations, earning interest on their investments. Exchanges play a crucial role in facilitating these transactions, connecting lenders with borrowers, and overseeing the process to ensure its success. In return for their services, exchanges collect fees or take a portion of the interest lenders earn, generating revenue for their platform.
Cryptocurrency exchanges can also offer a platform for users to buy and sell assets, known as a crypto marketplace. This marketplace allows users to trade digital assets such as NFTs, cryptocurrencies, and more traditional products like Bitrefill gift cards and phone refills. The exchanges generate revenue by charging trading fees, a percentage of the transaction volume, or a fixed amount per trade.

Token Launchpad
Exchanges generate revenue from token launchpads through listing fees, which projects must pay to launch their tokens on the exchange's platform. This fee covers costs such as due diligence, legal compliance, technical integration, and marketing efforts to promote the token sale. The listing fee structure can vary between exchanges and depends on the project's size or requirements, with some exchanges offering tiered pricing.
Exchanges may also secure supplementary revenue-sharing arrangements with projects besides listing fees. This can include receiving a portion of the tokens allocated to the exchange as part of the token distribution or obtaining a percentage of the project's future revenues. These agreements can generate recurring revenue streams for exchanges, particularly if the project becomes successful and generates significant income.
In addition, token launchpads provided by exchanges can offer extra benefits to projects, such as marketing assistance, consulting, managing the token sale, and technical support. By charging fees for these additional services, exchanges can generate extra revenue and offer a complete package to aid projects in successfully navigating the token launch procedure.
It is essential to mention that token launch platforms also have advantages for exchanges by drawing in new users and boosting trading activity. When token launches are successful, trading volume often rises as investors trade newly listed tokens. This increased trading activity generates fees from transactions.
Additional Services that Complement Each Other
Crypto exchanges can also generate revenue through complementary services such as connected games or decentralized applications (DApps). By partnering with game developers, exchanges can offer the necessary infrastructure, liquidity, and access to their user base. In return, they can earn a percentage of the transactions or fees generated within these games. This mutually beneficial revenue-sharing model encourages user engagement and promotes growth within the ecosystem.
Cryptocurrency exchanges can team up with prepaid card issuers to provide users with debit cards or prepaid cards connected to their exchange accounts, enabling them to use cryptocurrencies for real-world transactions. This collaboration can generate revenue for exchanges through card issuance fees, transaction fees, or revenue sharing with the prepaid card provider. By incorporating cryptocurrencies into everyday spending, this integration promotes the broader use of cryptocurrencies and contributes to its increased adoption.
Premium Services and Referral Programs
Certain crypto exchanges provide premium subscription options to expand their income sources, granting users exclusive access to distinct features and advantages. These exchanges offer different paid monthly subscription levels, with benefits such as lower trading fees, higher interest rates on cryptocurrency lending, and increased limits for buying and withdrawing funds.
An instance of this is Coinbase's offering, Coinbase One, which requires a monthly payment of $29.99 in exchange for no trading fees, access to advanced trading tools, increased staking rewards, and priority support. These subscription options are aimed at experienced users, traders, and institutions who engage in frequent transactions and wish to optimize the advantages available to their accounts.
Additionally, numerous crypto exchanges also pay existing users commissions for referring new customers. These referral programs are created to incentivize users to recommend the platform to colleagues and followers on social media or other channels. For instance, Binance provides a beneficial referral program with multiple levels, granting up to 40% in ongoing commissions based on the trading fees of referred users. Coinbase has its own referral program, rewarding $10 in Bitcoin for every new user referred.
Although referral programs may diminish potential revenue, the advantages of acquiring new customers through such programs outweigh the costs for exchanges. Attracting fresh, engaged traders is pivotal in boosting transaction volume and associated fees.
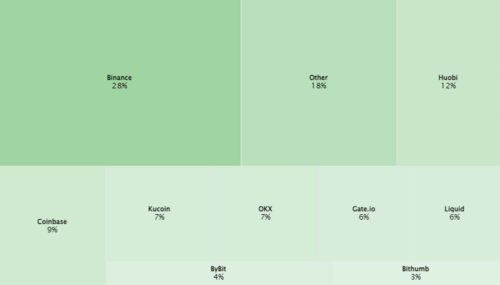
Key Players in Crypto. Source: Statista Market Insights
Important Insights
The key takeaway is that an exchange needs active users who generate a steady income through trading activities. The more users a platform has, the higher the volume of trading commissions, resulting in a more stable financial situation. It’s also advantageous that many exchanges have weathered the market downturns with style, grace, and dignity.
The popularity of cryptocurrency trading platforms has skyrocketed in recent years, with millions globally utilizing these exchanges to buy, sell, and trade digital assets. According to recent studies, the global revenue in the crypto market was valued at $18.5 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach $64.9 billion by 2027, with an impressive compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.40% between 2023 and 2027.
The cryptocurrency market is primarily controlled by centralized exchanges (CEX) that enable users to buy and sell cryptocurrencies quickly, efficiently, and securely. Nevertheless, decentralized exchanges (DEX) are gaining traction as they give users more autonomy over their assets and eliminate the need for intermediaries, offering a more secure and independent trading experience.
The success of cryptocurrency trading platforms will hinge on their versatility in response to shifting market dynamics. As the global crypto user base has grown to 673.90 million in 2023 and is projected to increase to 994.30 million by 2027, exchanges must demonstrate agility in the face of unpredictable market fluctuations and embrace new trends as they emerge.
In the upcoming article, we'll take a closer look at the leading crypto exchanges, their revenue streams, and their respective peaks and valleys. Additionally, we'll explore the realm of decentralized exchanges and how various cryptocurrency businesses demonstrate their ability to transform limited resources into thriving ventures at an impressive pace.
This article is provided for informational purposes only. It is not offered or intended to be used as legal, tax, investment, financial, or other advice.

Also published @ Substack.com; BeforeIt’sNews.com; Medium; Steemit.com.
Bruce Jacobs


.png)